Summer has faded in the UK with autumn bringing in rain showers, wind and turning leaves. We have begun the task of telling people about the Arabic Symbol Dictionary at conferences with paper and poster presentations. At ICCHP 2014 the Project Possibility University of Southampton students presented Symbol Dragoman using the symbol and word lists already gathered for the symbol dictionary along with the Tatoeba lists. This was followed up by Communication Matters 2014 where we had a poster and will be writing a paper. We have also just heard that we have been accepted for poster and paper presentations at TechShare Middle East, the Qatar Foundation Annual Research Conference (ARC’14) and RAATE 2014.
In Qatar, Nadine joined the research team with Mada as a speech and language therapist whilst also supporting AAC users at the Shafallah Center and Dana has come on board as a graphic designer just when we need to be thinking about logos, leaflets, updated posters and beginning the task of adapting or adding to the symbol set we wish to use. The ARASAAC team have kindly agreed to collaborate with us on the task of using their creative commons licensed symbols where appropriate for the dictionary. This was discussed as a result of the voting that took place in June and July.
During August and September Nadine and Tullah have been researching the issues around gathering core vocabularies in Arabic that are suitable for AAC users as well as considering the concerns around the enhancement of literacy skills which are challenged by the diglossic nature of Arabic. Levin et al (2008) mention the fact that “research has shown that the linguistic distance between Standard Arabic, the language of print, and spoken Arabic vernacular, the oral language of children challenges the acquisition of reading in Arabic (Abu-Rabia, 2000; Saiegh-Haddad, 2003a, 2004, 2005, 2007a).” It appears to affect all aspects including “lexicon, syntax, morphology and phonology”. It is felt that by offering sound patterns of lexical entries (with the use of recorded and synthesised text to speech) this could support carers and teachers of speech impaired individuals when working on literacy skill acquisition.
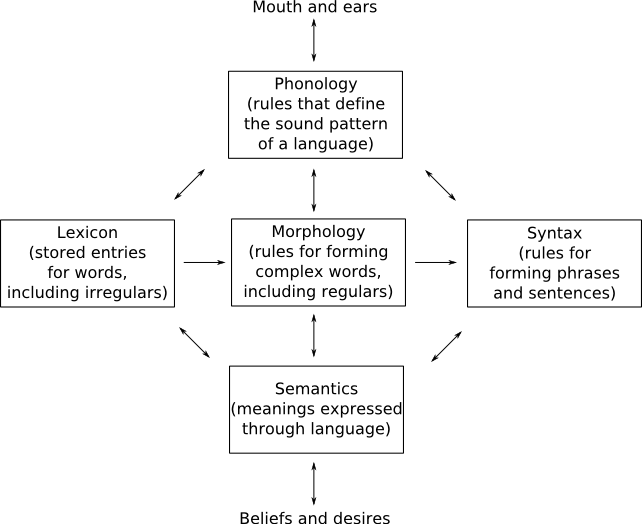
Reproduced under fair use Copyright © 1999 Stephen Pinker (Mark McConville and Henry S. Thompson, 2 February 2012)
So discussions have continued around phonemic segmentation and how this will be represented in the dictionary for both Arabic and English with the result of changes being made to the symbol manager system. It appears that in Arabic the phonemic segmentation can be generated almost automatically with the help of some clever computer coding as long as the diacritics are in place – that is according to Nawar!
Levin et al have cited several researchers in their comment that the sub-syllabic level (Consonant Vowel level (CV)) in Arabic phonemic segmentation is more easily learnt compared to any other way of encouraging phonemic awareness. A study with bilingual children by i Saiegh-Haddad & Geva (2008) showed that being able to sound out parts of words when learning to read was equally important in Arabic as in English. However, when it comes to deciding which section in a word forms a phonemic segment there is a rather more torturous route for English words which will require manual entry for consonant blends and digraphs etc. Spaces between the segments will be used when adding words to the Symbol Manager.
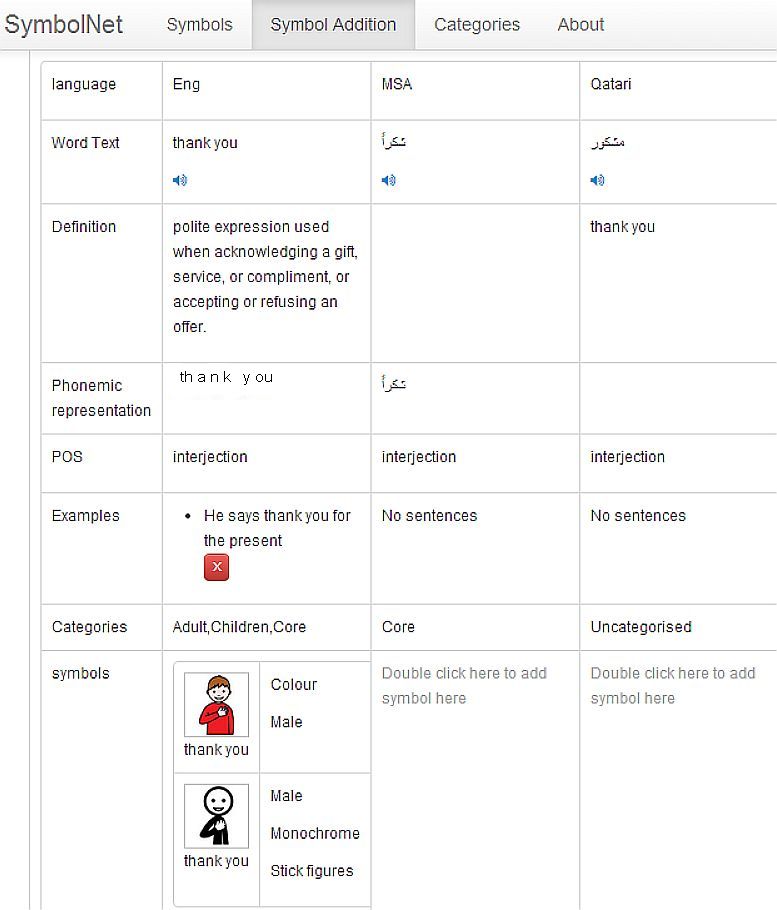
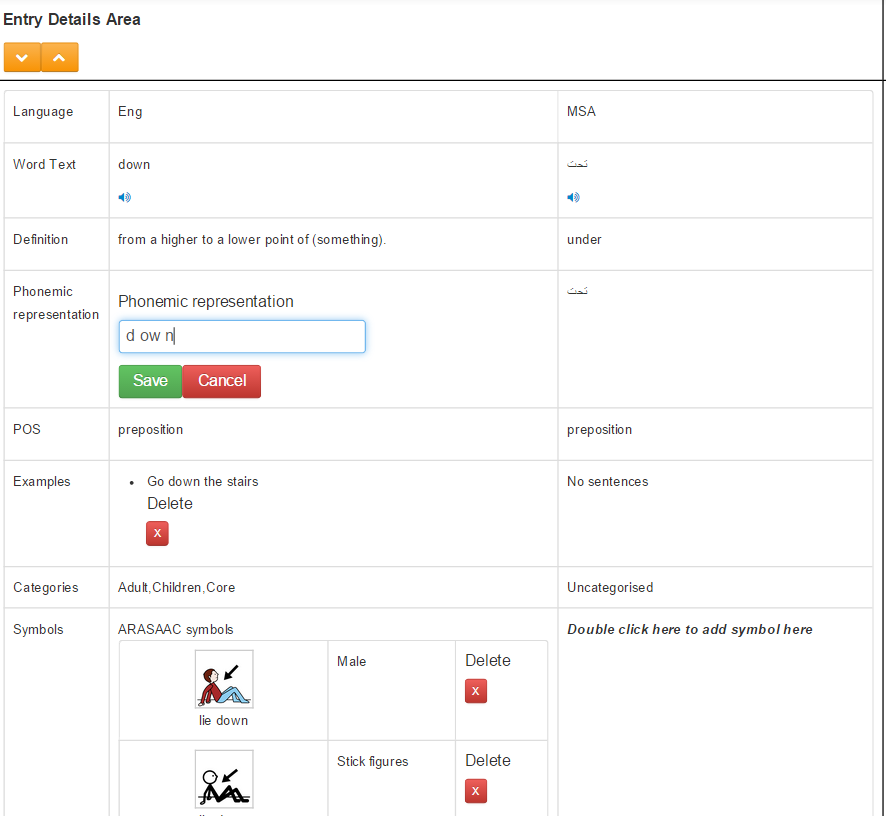 As a result of the changes made to the system the team at Southampton university have been beta testing the latest version. Early trials have been completed and the system is ready for the addition of new lexical entries with definitions, sentences for context, categorise for browsing and searching, parts of speech and the extra field for phonemic segmentation. New symbols can be added with categories such as monochrome, colour and gender. All items will be distinguished by their language English, Modern Standard Arabic and Qatari. The latest version is faster and accesssible using mouse, keyboard only or touch screen. Nawar has worked hard to make it as flexible as possible and it is now ready for further testing using a simple check list – download MS Word doc Beta Testing Symbol Manager v1 . We have also used the SUS evaluation scale (Brooke, 1996). Taking an iterative approach with the participation of as many interested parties as possible we have setup up logins for the Symbol Manager System and will be reacting to any feedback we receive from those involved with the project.
As a result of the changes made to the system the team at Southampton university have been beta testing the latest version. Early trials have been completed and the system is ready for the addition of new lexical entries with definitions, sentences for context, categorise for browsing and searching, parts of speech and the extra field for phonemic segmentation. New symbols can be added with categories such as monochrome, colour and gender. All items will be distinguished by their language English, Modern Standard Arabic and Qatari. The latest version is faster and accesssible using mouse, keyboard only or touch screen. Nawar has worked hard to make it as flexible as possible and it is now ready for further testing using a simple check list – download MS Word doc Beta Testing Symbol Manager v1 . We have also used the SUS evaluation scale (Brooke, 1996). Taking an iterative approach with the participation of as many interested parties as possible we have setup up logins for the Symbol Manager System and will be reacting to any feedback we receive from those involved with the project.
References
Brooke, J. (1996). SUS: A “quick and dirty” usability scale. In P. W. Jordan, B. Thomas, B. A.
Weerdmeester, & A. L. McClelland (Eds.), Usability Evaluation in Industry. London: Taylor
and Francis.
Levin, I., Saiegh-Haddad, E., Hende, N., & Ziv, M. (2008). Early literacy in Arabic: An intervention study among Israeli Palestinian kindergartners. Applied Psycholinguistics. Accessed 12th October 2014, http://journals.cambridge.org/action/displayAbstract?fromPage=online&aid=1899796
Saiegh-Haddad, E., & Geva, E. (2008). Morphological awareness, phonological awareness, and reading in English-Arabic bilingual children. Reading and Writing, 21(5), 481–504. Accessed 12th October 2014 http://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs11145-007-9074-x