Communication Matters held a very interesting day on ‘AAC, Literacy and Complex Needs’ with Jane Farrall and Sally Clendon leading the day. There were detailed handouts to keep us on track and similar slides have been put on slideshare when the two speech therapists presented on the subject at the ICCHP conference in 2014
Here are some notes that I made that are relevant to a bilingual Arabic / English situation as many of the specifics during the day were related just to the English language.
Looking at Literacy in the round
Giving AAC users a reason to learn to read and write by always:
- Reading to and with children constantly providing examples of text structures
- Sharing reading experiences that are relevant to their daily life and can be part of an ongoing dialogue
- Making sure the reading exercise has a function, needs thinking about beyond the pictures/symbols
- introducing ways of using text as part of daily life, such as sharing ‘to do’ lists, shopping lists etc so AAC users experience the concept of text in action not just as a passive exercise.
Techniques
Introducing small flip charts or core boards that have symbols that can be used to indicate understanding of a page of text when it has been read so that there is engagement. Their use can be reduced as text is understood and letters then words are used on the small flip charts.
Repetition and time is key. The charts can help with the increase of vocabulary and become part of daily communication charts.
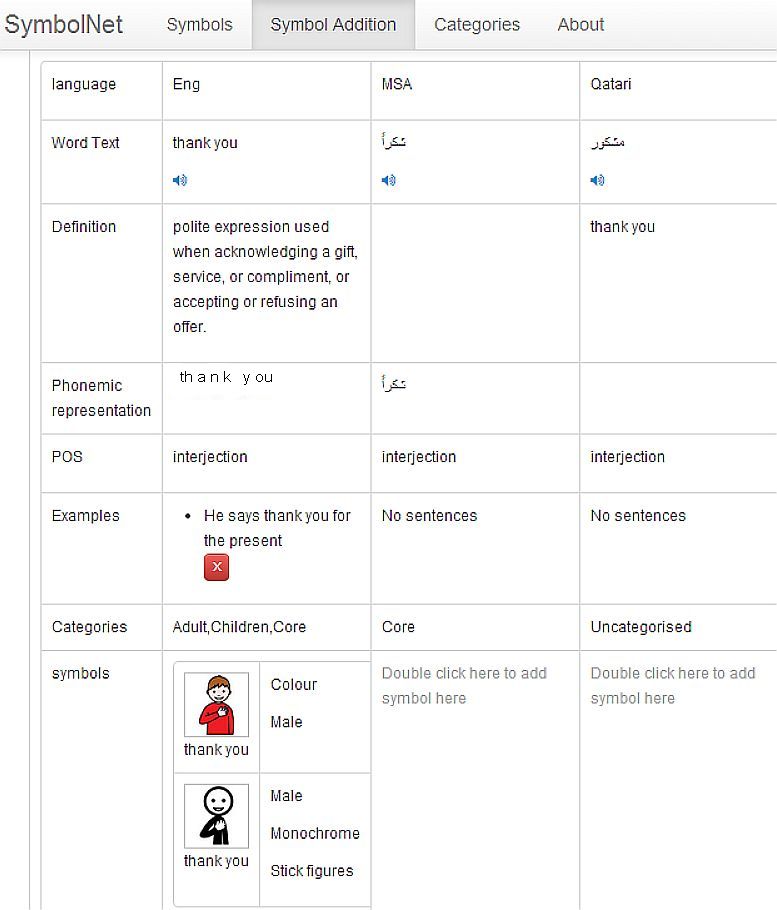
Technology including the use of iPads, Clicker, Boardmaker and eventually CoWriter were discussed. Interactive ebooks and large picture books. Big Macks and Step by Step can provide repeated lines with speech and recorded comments for the AAC user. Jane Farrell has collected many English resources. The Tawasol team will be making some examples in Arabic.
Several terms used throughout the day will be recognised by speech and language therapists such as
- Modelling where those communicating with an AAC user constantly use a symbol / text system such as PODD and ADL plus choice charts to interact in the conversation.
- Pragmatic Organisation Dynamic Displays (PODD) are communication books/devices that have organised sets of symbols/words to encourage modelling and communication in every situation. The charts/boards are made up of symbols representing both core and fringe vocabularies to suit individual users and tend to have a full range of vocabulary to encourage exploration in new communication situations. To gain increased repetition of vocabulary
- Aided Language Displays (ADL) are used with frequently needed symbols/words and choice or topic charts are used with specific tasks such as reading a book with some core vocabulary but also words specific to the story. Jane Farrall stresses that these small vocabulary boards should only be used in conjunction with the wider vocabulary – core /PODD symbol sets to encourage increased communication
“Instead of making a morning circle page, we should teach the students to go to chat or social vocabulary to say hello and then onto people to use someone’s name. We should teach them to go to the weather section of their system to tell us about the weather and then onto descriptions to make a comment about it. And we should demonstrate using these skills whenever we greet people or comment about the weather throughout the day – and not just in morning circle and definitely not just at school. This is how we get overall communication development, including language and vocabulary development.” (Jane Farrall, Oct 2015)
Structured Reading
General points made:
- Reading and waiting for reactions to comments, pausing from 5 – 30 seconds to allow the listener to engage. Shared reading, asking questions, pausing again and responding by adding hints or clues to a possible answer.
- Integrating the AAC user’s communication system within the reading situation so that, for instance a topic can be related to the reading or particular activities are relevant to the words being learnt. For example take a chart showing fruit – when fruit is mentioned discuss their favourite type – modelling and chatting about it with the expectation of an interactive experience.
- Create books with a main picture or symbol and text – making a story that can be shared, personalised and therefore meaningful. See Tar Heel Reader for free examples and the Tawasol Team will be adding some to their Resources pages. Jane Farrall has a blog about putting “Tar Heel Reader books into iBooks – with Speech!”
- More information on guided reading by Jane Farrall with links to useful iPad apps
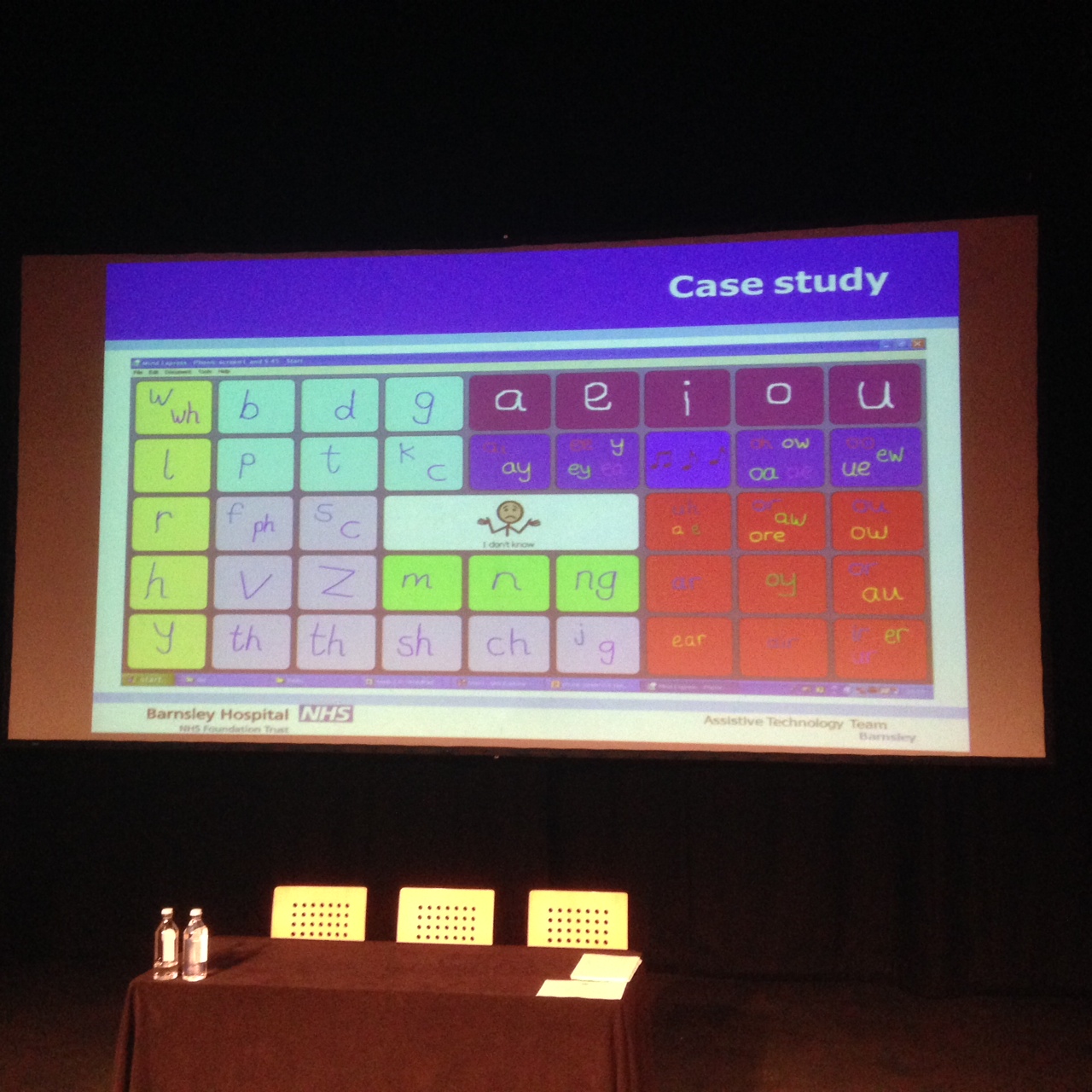
The day continued with the introduction of letters, phonological awareness to phoneme-focused interventions, words and so on and finally into writing. There were examples of comparing letter sounds and blending, onset and rime etc.
The use of Word Walls with high frequency words and key word patterns. Those words often used in the environment and finally words that are often mispelt when moving into writing. Design portable word walls over three sheets of A4 and laminated. You can use Velcro with individual letters, words or sounds or symbols. Simple A4 Portable word wall template download
References about modelling, PODD and ADL provided by Novita Children’s Services, Australia
Binger, C. & Light, J. (2007) The effect of aided AAC modeling on the expression of multi-symbol messages by preschoolers who use AAC. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 23, (1) 30 – 43.
Bruno, J. & Trembath, D. (2006) Use of aided language stimulation to improve syntactic performance during a weeklong intervention program. Augmentative and Alternative Communication, 22(4).
Cafiero, J. (2001) The Effect of an Augmentative Communication Intervention on the Communication, Behavior, and Academic Program of an Adolescent with Autism. Focus on Autism and Other Developmental Disabilities, Vol. 16, No. 3, 179-189.
Drager, K, Postal, V, Carrolus, L, Gagliano, C & Glynn, J. (2006) The Effect of Aided Language Modeling on Symbol Comprehension and Production in 2 Preschoolers With Autism. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 15; 112-125.
Harris, M. & Reichle, J. (2004) The Impact of Aided Language Stimulation on Symbol Comprehension and Production in Children With Moderate Cognitive Disabilities. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology Vol.13 155-167.
Porter, G. (2007) Pragmatic Organisation Dynamic Display (PODD) communication books: Direct access templates. Melbourne: Cerebral Palsy Education Centre.
Porter, G. (2008) Pragmatic Organization Dynamic Display (PODD) communication books: Direct access templates. US Letter paper version. Melbourne: Cerebral Palsy Education Centre.
Porter, G. (2009) Advanced PODD Workshop. Melbourne: Cerebral Palsy Education Centre.
Roman-Lantzy, C. (2007) Cortical Visual Impairment: An Approach to Assessment and Intervention. New York: AFB Press. American Foundation for the Blind.