There is a consensus that Arabic dictionaries,
whether printed or electronic are not user-friendly.
Rather than being tools for learning, they are a
hindrance. Their complexity and their presentations are
not conducive to learning. Consequently, their impact
on vocabulary acquisition, even though not formally
assessed, is highly negative. (Belkhouche et al, 2011)
The authors of the paper go on to say that “the printed Arabic dictionary provides a low quality, a poor presentation, a disorganized structure, and an unscientific approach. A cursory browsing of Arabic dictionaries on the library shelves highlights these deficiencies.“
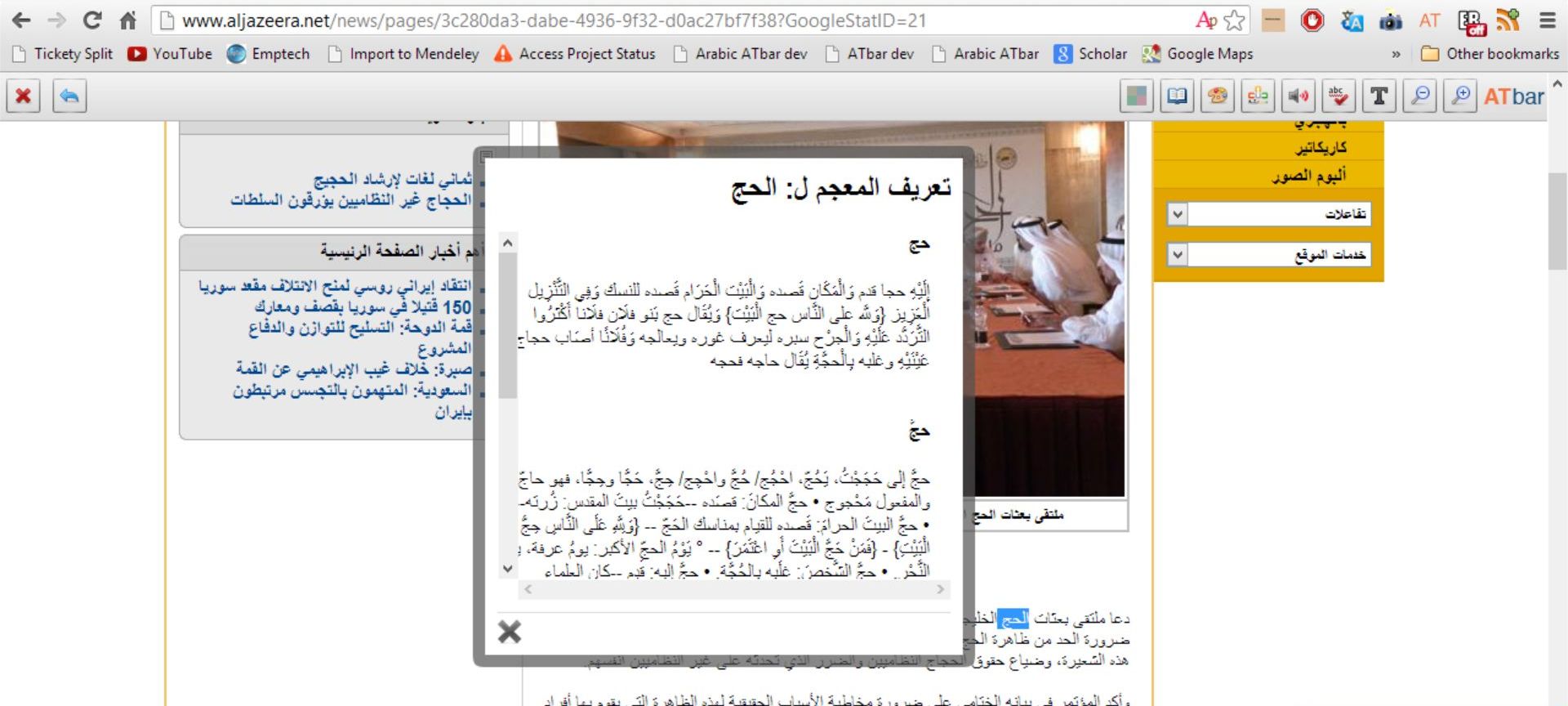
Nawar and Magnus have completed the work on a new online Arabic dictionary. This has now become part of the standard Arabic ATbar and we would be very grateful if it could be tested as much as possible.
Nawar tells me that “the dictionary database includes data from two modernized Arabic dictionaries (for word look-ups) and one traditional dictionary for root look-ups. More data can be easily added in. The dictionary plugin does not only use exact match to search for words and roots in the database, but also, it uses a light stemming algorithm to increase the reliability of the search. Prefixes and suffixes and the definite articles are removed if exact matching does not return results. The order in which these prefixes and suffixes are removed is not random but based on knowledge in the language and has been tested before for applications in information retrieval.”
The method used by Nawar was based on a paper written by Halabi et al (2010) on “A Hybrid Approach for Indexing and Retrieval of Archaeological Textual Information”
The suggested hybrid retrieval approach employs various clustering and
classification methods that enhances both retrieval and presentation, and infers
further information from the results returned by a primary retrieval engine,
which, in turn, uses Latent Semantic Analysis (LSA) as a primary retrieval
method. In addition, a stemmer for Arabic words was designed and
implemented to facilitate the indexing process and to enhance the quality of
retrieval.
The dictionary database was then set up by Magnus to link with any words selected on a web page and depending on the choice of a root or the word for a definition – results are shown in what is hoped to be the most helpful way possible.
We are incredibly grateful to the work of Nawar and his brother as well as Magnus as we feel this is a first in terms of how a dictionary can be presented as an online browser plugin to support those reading Arabic texts. We are aware more dictionaries can be added and possible improvements can be made, but we need feedback as to how useful this dictionary is to users. Please leave comments!